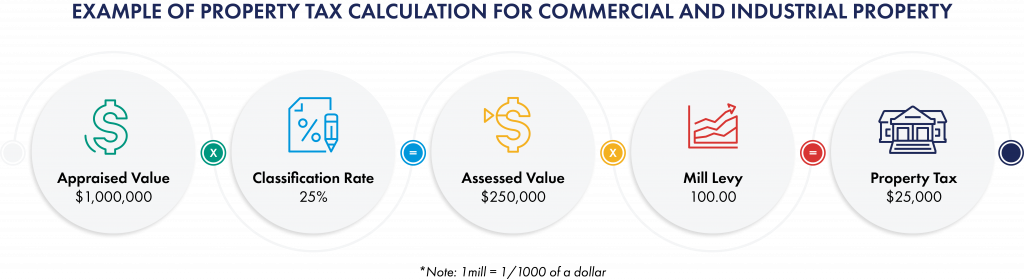
Both real and tangible personal property are subject to ad valorem taxation by cities, counties and special taxing districts. Intangible property, to the extent it is taxable, is classified and taxed separately. All property is appraised at its fair market value, except for agricultural land, commercial and industrial personal property and certain vehicles. The assessment rate set forth in Art. 11, § 1 of the Kansas Constitution and K.S.A. 79-1439 is applied to the appraised value to determine the assessed value.
The rate of tax depends on the levy of the local taxing district and will vary within the state by location. Both real and tangible personal property are assessed by the county appraiser in the taxing district in which the property is located. Taxes are paid to the county treasurer.
Property taxation is administered by the Division of Property Valuation of the Department of Revenue together with local taxing officers. Public utilities are treated separately for property tax purposes. Utility property is assessed and apportioned to local taxing districts by the Division of Property Valuation.
There are several property tax exemptions that may be available to businesses for certain qualifying real and tangible personal property. The Board of Tax Appeals or appeals courts will decide whether a specific property qualifies for exemption. There are a few exceptions to the filing requirement including machinery and equipment qualifying for exemption pursuant to K.S.A. 79-223 or K.S.A. 79-224 and items of business machinery, equipment and supplies qualifying for exemption pursuant to K.S.A. 79-201w. (K.S.A. 79-213(l)).
The request for exemption shall be filed with the county appraiser of the county where such property is principally located.
After a review of the exemption request, and after a preliminary examination of the facts as provided, the county appraiser shall recommend to the Board of Tax Appeals that the exemption request either be granted or denied, and may request, a hearing be held.
If a denial is recommended, a statement of the controlling facts and law relied upon shall be included on the form. The final decision will be made by the Kansas board of Tax Appeals. (K.S.A 79-213)
Cities, counties and townships can levy taxes on intangible property. Counties may tax such property at a rate of up to 0.75 percent, and cities or townships may impose an intangible property tax of up to 2.25 percent. The total intangible property tax burden of any individual or business cannot exceed three percent. In practice, most local governments have no tax on intangible property.
One-third of the counties in Kansas, less than one-fifth of the cities and about one-third of the townships impose such a tax.
Intangible property is defined as monies and credits including gold and silver coin, United States Treasury notes and stock certificates otherwise taxable to the owner or holder. Intangibles also include notes, bonds and debentures; claims secured by deed; liquidated claims and demands for money; accounts receivable; and all written instruments, contracts or other writings evidencing, calling for, fixing or showing a fixed obligation in favor of the owner.